DRBFM
– Design Review Based on Failure Mode –

Introduction to Design Review Based on Failure Mode (DRBFM)
Design Review Based on Failure Mode (DRBFM) was created by Tatsuhiko Yoshimura, (Toyota). It is based off the approach that accidents are, considered to be, avoidable if found during the development of a design. Improper designs contribute to reduction in brand image, poor reliability and negative financial impacts. Many companies battle with the improvement process to mitigate design risk and often brainstorm updates to processes rather than determine actions to change the designs.
DRBFM is a visual process that may link to Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) and Fault Tree Analysis (FTA), based on experience. Each member compares “good design” to the intentional changes and predicts possible failures. With the use of GD3 and brainstorming techniques, it evaluates design and manufacturing with respect to the technical causes. The method creates a robust format for problem solving.
What is Design Review Based on Failure Mode (DRBFM)
DRBFM is a cross functional disciplined process used to evaluate proposed changes to designs. The model is comprised of three core parts:
- Problem solving: A disciplined method used to solve complex issues
- Recurrence prevention: The use of a collection of processes within a system designed to prevent recurrence related to the problem-solving methodology
- Proactive prevention: A process to search for hidden issues in new or changed designs
DRBFM also focuses on proactive prevention using the GD3 approach:
- Good Design:
- Reliable designs contributing to customer satisfaction
- Good Discussion:
- Review of current design with respect to “Good Design”
- Good Design Review:
- Problem discovery and mitigation
How to Perform Design Review Based on Failure Mode (DRBFM)
The systematic approached is used to create a comprehensive procedure that is proactive, ensuring a global view of the product hierarchy. This provides a map to ensure all levels of communication are addressed. These interactions contribute to including not only the designer, but the full system communication.
The following steps outline the process that applies mainly to intentional changes to designs, however can be applied to new designs while incorporating tools such as FMEA and FTA. When starting with an FMEA, focus on the components that are associated with the ‘deliberate change’. The DRBFM should be started on prototype drawings to increase the effectiveness of the process.
- Select the team based on the system and interactions (based on design change)
- Include representation from system, sub systems and components
- If this fails, the entire process will suffer
- Include representation from system, sub systems and components
- Visualize the differences between the changes with respect to the “Good Design”
- Scope must be identified to the change
- Since most companies spend their time identifying issues without properly resolving them or ignoring the solution altogether, the team needs to stay within the defined scope. Facilitation can help manage the team’s focus and ensure the team understands what may adversely affect an already proven feature or features within the “Good Design”.
- If the ‘contents of the change’ are not shared by the designer, process suffers
- The FMEA process is used to determine details based on the functions affected by the ‘intentional change’
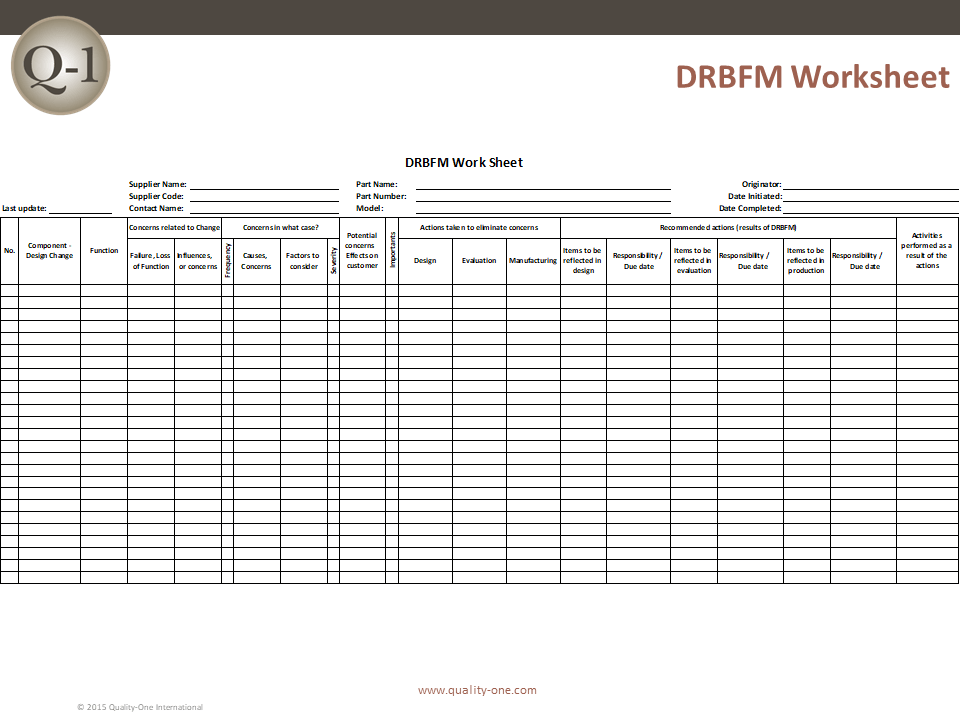
- Information is then transferred from the FMEA to the left hand columns on the DRBFM worksheet
- Note: this is the responsibility of the designer
- All participants must participate from item #1
- Discussion begins on the right hand side of the DRBFM worksheet
- Interactions between components will correlate to interactions between sub systems and system. Therefore, anything that is not understood at the feature or component change will be seen at higher level functions.
- Scope must be identified to the change
- “Good Discussion” begins on the possible problems related to the intended change
- Assemble all drawings, component examples, similar designs, etc.
- Designers should prepare for a constructive debate regarding the change ‘function of the target part’
- The facilitator is responsible for the success of the review
- They are responsible for keeping the tension at an acceptable level to spark ideas without turning offensive
- The rest of the participants should be prepared to offer their ideas and experience
- Try to keep total number of participants between 10 and 15 (at most)
- ‘Predicting the concerns of the change’ by carefully considering the interactions based on the change (review by looking, disassembling, comparing, measuring, include surrounding areas – interactions, customer viewpoint, etc.)
- ‘Cause of concerns (detailed review)’ – The majority of failures occur due to interactions
- Consider stresses, forces, corrosion, oils, surfactants, temperature, handling, fasteners, correlation to the manufacturing process (Process FMEA), etc.
- Review one component / concern at a time. FTA may be a useful tool for this part of the process.
- If concerns are identified, they must be mitigated
- Review conventional methods of design mitigation (lower risk)
- Items left will stand out requiring more focus to resolve using the DRBFM process ‘unnoticed point inspection’ (includes past failures)
- Enter actions as design, evaluation or process
- Include responsible department, person and due date
- All are documented in the DRBFM Worksheet as identified in the meetings
- If this is delayed, items will accrue and render the team stuck
- ‘Measures for all concerns’ – “Good Design Review”
- Passively verify all actions are implemented into the drawings, evaluations and process design
- Actively verify on completed test parts and review (wear, disassembled, cut, etc.)
- All causes identified are now reviewed by the designer to determine if they are associated with specific measures. (Note: it is very difficult to change or validate if there is no baseline to measure against)
Design Review Based on Failure Mode (DRBFM) Services
The DRBFM Services available from Quality-One are DRBFM Consulting, DRBFM Training and DRBFM Support, which may include Facilitation, Auditing or Contract Services. Our experienced team of highly trained professionals will provide a customized approach for developing your people and processes based on your unique DRBFM needs. Whether you need Consulting to assist with a plan to deploy DRBFM, Training to help understand and drive improvement or hands-on Project Support for building and implementing your DRBFM process, Quality-One can support you! By utilizing our experienced Subject Matter Experts (SME) to work with your teams, Quality-One can help you appreciate the value of DRBFM in your organization.
Learn More About Design Review Based on Failure Mode (DRBFM)
Quality-One offers Quality and Reliability Support for Product and Process Development through Consulting, Training and Project Support. Quality-One provides Knowledge, Guidance and Direction in Quality and Reliability activities, tailored to your unique wants, needs and desires. Let us help you Discover the Value of DRBFM Consulting, DRBFM Training or DRBFM Project Support.