FMEA Training (Onsite)
– Training at Your Facility –
⇓ FMEA Training Course Details
⇓ FMEA Training Course Description
⇓ FMEA Training Course Objectives

FMEA Training Course Details (Onsite)
Quality-One brings the knowledge to your location, resulting in immediate benefits for your team. This option is convenient for scheduling and provides an opportunity to train the whole team to utilize Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA). Onsite technical training is most popular with organizations that require five or more participants to be trained. Expenses are minimal compared to having the team travel.
FMEA Training Course Description (Onsite)
This course follows a step-by-step method for conducting FMEA in a dynamic instructor-led format. The course describes the methodologies which have been proven to be best practices for FMEA development.
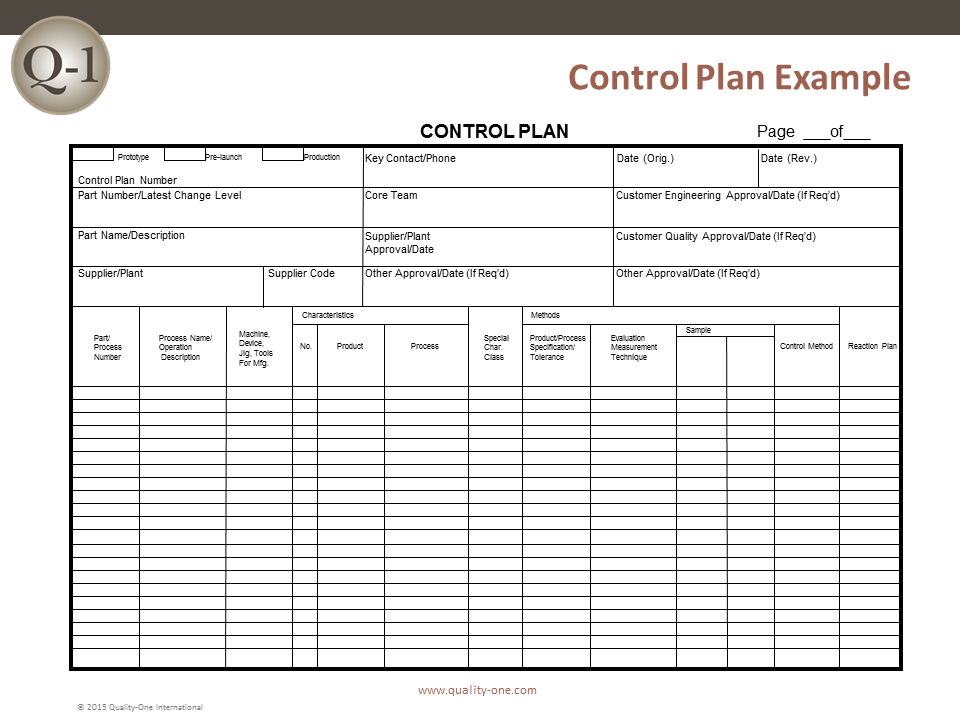
Each participant will have the opportunity to develop all the elements of a Design and Process FMEA, including use of robustness tools, Process Flow Charts and Control Plans. All activities will include industry-specific examples and terminology.
Participants will learn how to assess risk and determine the levels of risk that trigger mitigation actions. Action plans derived from FMEAs and methods to manage FMEA data for future use are also covered in detail. Participants can expect team activities and relevant exercises in a workshop format. The Quality-One reference materials and examples also provide an invaluable resource for review long after the training.
FMEA Training Course Objectives (Onsite)
The objectives of Quality-One FMEA onsite training courses are to:
- Perform Product and Process FMEAs
- Link FMEA to Product Development Process and Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP)
- Facilitate a FMEA
- Participate in the development of a Design and Process FMEA
- Define risk and determine levels of risk requiring mitigation
- Set up an effective Cross Functional Team (CFT) required for FMEA Development
- Efficiently select Severity, Occurrence and Detection rankings
- Implement a Risk Priority Number (RPN) reduction process
- Determine design and process special characteristics
- Understand and demonstrate the links between Design FMEA and Process FMEA
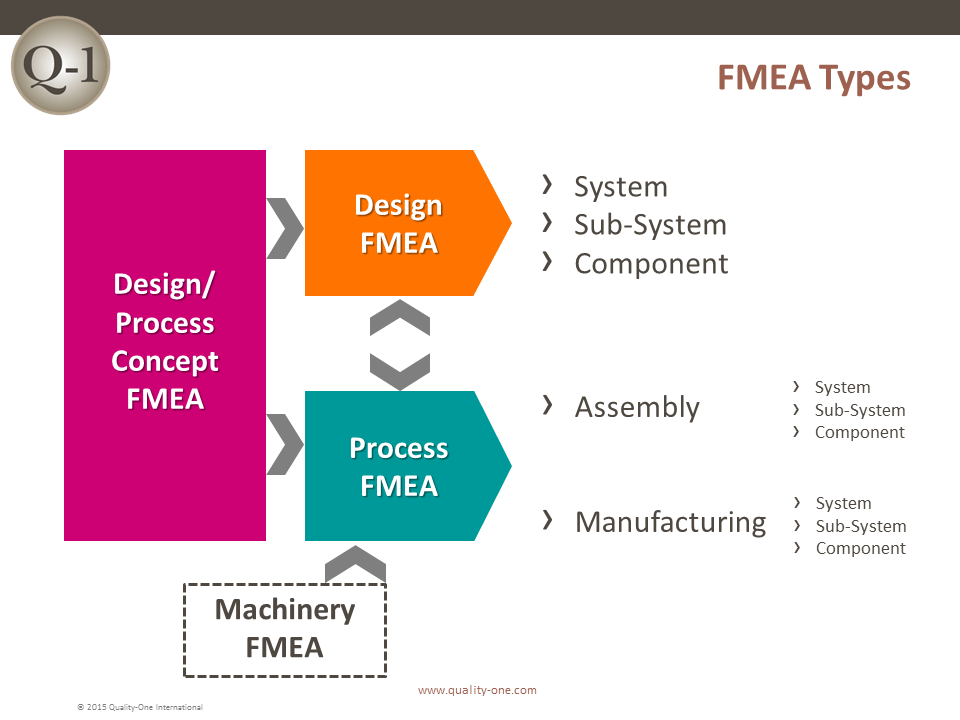
- Understand the different types of Design and Process FMEAs
- System
- Subsystem
- Component
- Assembly
- Manufacturing
- Create and manage action plans derived from FMEA
- Manage and store FMEA content for future use
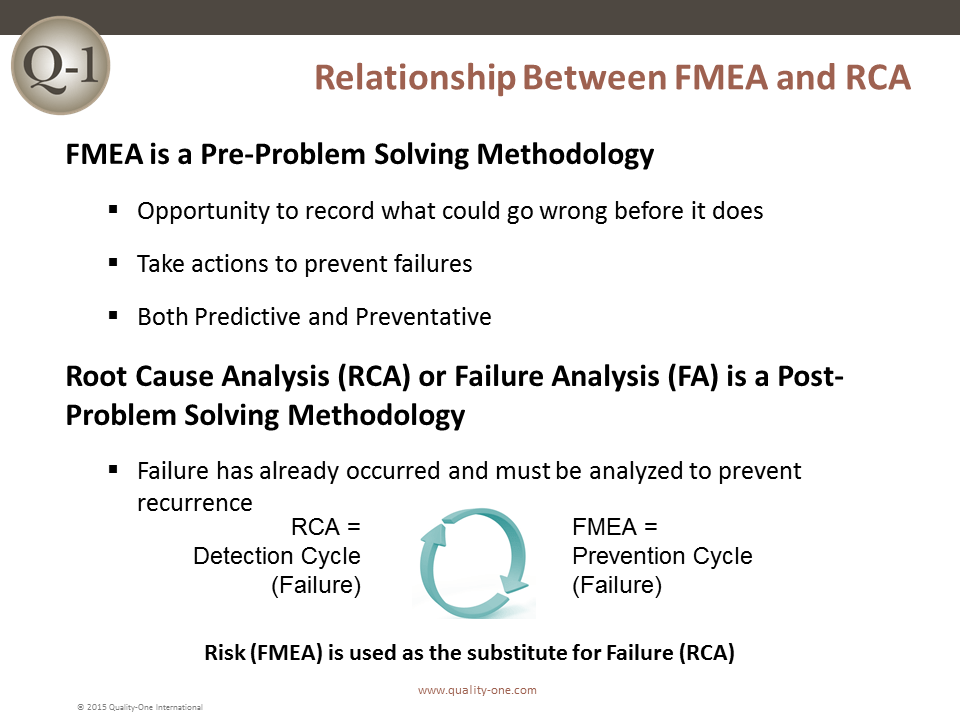
- Understand links between FMEA and problem solving methods, such as:
- Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
- 5 Why
- Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
- A3
- Plan Do Check Act (PDCA)
- Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control (DMAIC)
- Design for Six Sigma (DFSS)
- Understand links to Control Plan Methodology. Save time and cost that come with sending associates to conferences and seminars at offsite locations.
FMEA Training Course Outline (Onsite)
Here’s the outline of our failure mode and effect analysis training course:
FMEA Process Overview
- Introductions and course objectives
- The history and purpose of FMEA
FMEA Methodology
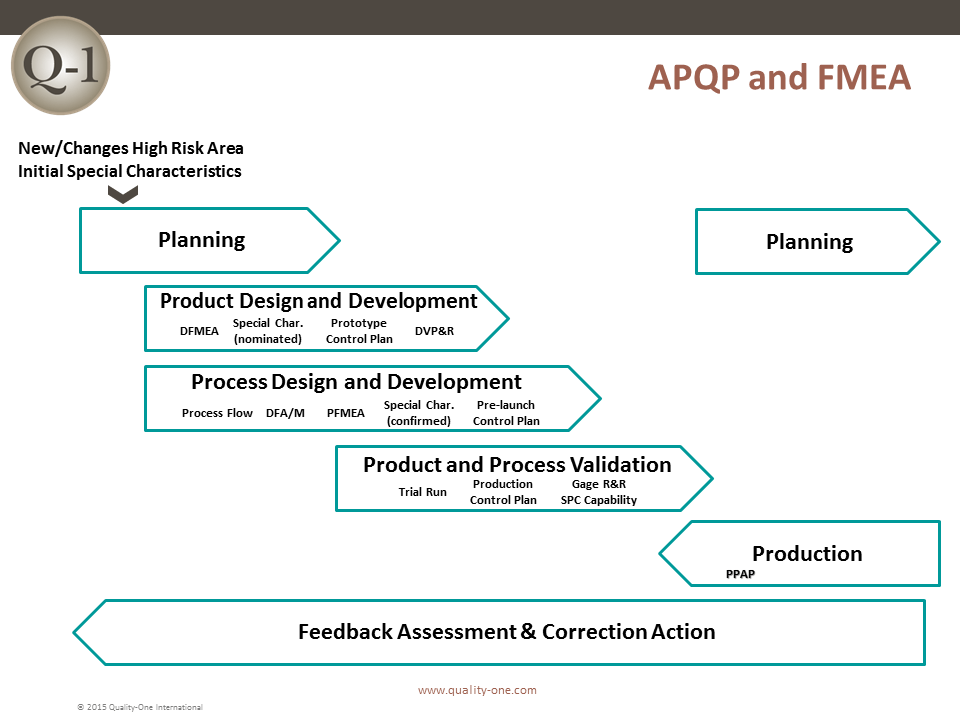
- FMEA in Product Development Process
- System / subsystem / component FMEA
- FMEA development methodology
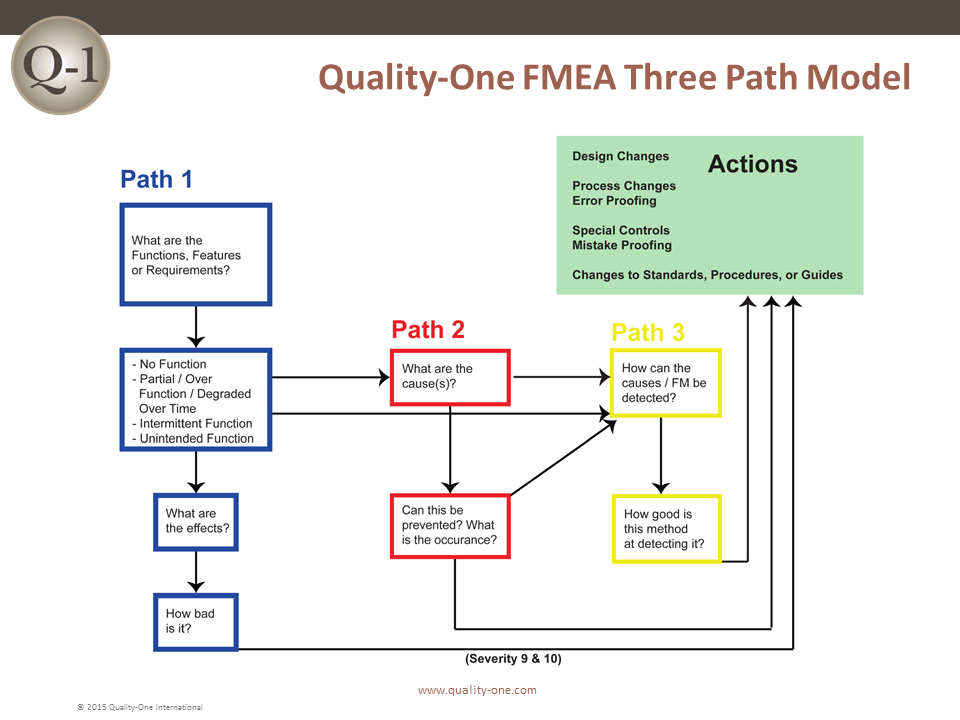
- The three path model
- Team structure and rules for efficiency
- Team membership for best results
FMEA Linkage and Collaboration
- The link between Design and Process FMEA
- Special Characteristics (Critical and Significant)
- Collaborative Product (Process) Development (CPD) on Special Characteristics
- Special Characteristics as inputs to PFMEA
- Tolerance Design and Process Capability Estimation
- What is Risk?
- Criticality (Severity X Occurrence)
- Risk Priority Number (RPN) and its use
- When to take action and developing action plans.
Practical application of the Design FMEA technique
Pre-work:
- Failure Mode Avoidance (FMA)
- Robustness tools (Noise factors to include in the FMEA)
- Interface analysis / Boundary Diagram
- Parameter Diagram
Methodology and hands on experience
- Path 1
- Item / Functions Requirements / Failure Modes / Effects of Failure / Severity
- Severity ranking guidelines reviewed with best practices
- Actions for High Severity (9 / 10)
- Path 2
- Causes / Prevention Controls / Occurrence
- Quality-One ION Technique for Cause development
- Occurrence ranking Guidelines with Best Practices
- Actions to eliminate and/or reduce cause probability
- Special Characteristics definition (Key Dimensions / Features)
- Error Proofing and Mistake Proofing (Poke Yoke)
- Path 3
- Test and verification methods
- Detection ranking guidelines
- Actions to improve tests and verification techniques
- RPN reduction
DFMEA Closure
- Design Review integration (Design Review Based on Failure Modes (DRBFM) concepts)
- Test Plan development (Design Verification Plan and Report (DVP&R))
- Revisit RPN Rankings after action completion
Practical Application of PFMEA
Pre-work:
- Failure Mode Avoidance (FMA)
- Process Flow Chart
- Characteristic Matrix
- Lean Value Stream Map (optional)
Methodology and hands on experience
- Path 1
- Process Name / Functions Requirements / Failure Modes / Effects of Failure / Severity
- Severity ranking guidelines review with best practices
- Actions for High Severity (9 / 10)
- Path 2
- Causes / Prevention Controls / Occurrence
- Ishikawa (6M’s) and Use of Quality-One Matrix for Cause development
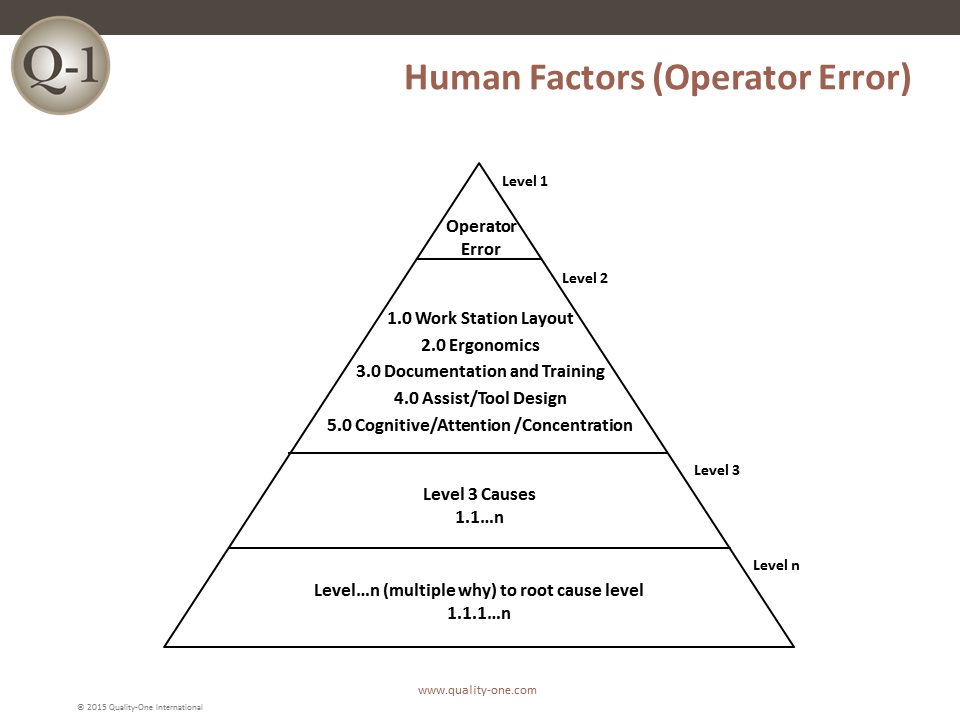
- Human Factors Engineering (Operator Error treatments)
- Occurrence ranking Guidelines with Best Practices
- Actions to eliminate and/or reduce cause probability
- Error Proofing for Human Error
- Path 3
- Test and verification methods for Causes and/or Failure Modes
- Detection ranking guidelines
- Actions to improve tests and verification techniques
Control Plan Relationships
- Pre-Launch Control Plan
- Production Control Plan
PFMEA Revisit FMEA RPN and Re-Rank
Managing FMEAs
Q&A and Closure
FMEA Training (Offsite)
– Training at Our Facility –
⇓ FMEA Training Course Details
⇓ FMEA Training Course Description
⇓ FMEA Training Course Objectives

FMEA Training Course Details (Offsite)
Quality-One Technical Training Centers provide an environment without interruption from daily activities. This FMEA course benefits individuals and organizations with less than five people requiring a working knowledge of Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA). The course is also held in a setting free of normal work interruptions, which increases knowledge transfer.
The activities are developed around principles that all participants (from diverse backgrounds) can relate to. Offsite training permits participants to interact with others from different disciplines and share different viewpoints and experiences. Discussing the unique challenges from various industries keeps interest high. Many times, best practices from one industry are often shared to the benefit of others.
FMEA Training Course Description (Offsite)
Offsite FMEA training follows a step-by-step method of conducting FMEA in an engaging instructor-led format. The course describes proven methodology for proper FMEA development. Each student will have the ability to develop a Design and Process FMEA including use of robustness tools, Process Flow Chart and Control Plans.
Participants will learn how to assess Risk and determine which levels of risk require mitigation. We’ll also cover action plans that result from FMEAs and ways to manage FMEA data for future use. Participants can expect team activities and relevant exercises in a workshop format. The Quality-One reference materials and examples also provide an invaluable resource for review time after time.
FMEA Training Course Objectives (Offsite)
The objectives of Quality-One FMEA offsite training courses are to:
- Perform Product and Process FMEAs
- Link FMEA to the Product Development Process and Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP)
- Facilitate a FMEA
- Participate in the development of a Design and Process FMEA
- Define Risk and determine levels of Risk requiring mitigation
- Set up an effective Cross Functional Team required for FMEA Development
- Efficiently select Severity, Occurrence and Detection rankings
- Implement a Risk Priority Number (RPN) reduction process
- Determine design and process special characteristics
- Understand and demonstrate the links between Design FMEA and Process FMEA
- Understand the different types of Design and Process FMEAs
- System
- Subsystem
- Component
- Assembly
- Manufacturing
- Create and manage action plans derived from FMEA
- Manage and store FMEA content for future use
- Understand links between FMEA and problem solving methods, such as:
- Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
- 5 Why
- Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
- A3
- Plan Do Check Act (PDCA)
- Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control (DMAIC)
- Design for Six Sigma (DFSS)
- Understand links to Control Plan Methodology. Save time and cost that come with sending associates to conferences and seminars at offsite locations.
FMEA Training Course Outline (Offsite)
Here’s an outline of the offsite FMEA training from Quality-One:
FMEA Process Overview
- Introductions and course objectives
- The history and purpose of FMEA
FMEA Methodology
- FMEA in Product Development Process
- System / subsystem / component FMEA
- FMEA development methodology
- The three path model
- Team structure and rules for efficiency
- Team membership for best results
FMEA Linkage and Collaboration
- The link between Design and Process FMEA
- Special Characteristics (Critical and Significant)
- Collaboration on special characteristics
- Special characteristics as inputs to PFMEA
- Tolerance Design and Process Capability Estimation
- What is Risk?
- Criticality (Severity X Occurrence)
- Risk Priority Number (RPN) and its use
- When to take action and development of action plans.
Practical application of the Design FMEA technique
Pre-work:
- Failure Mode Avoidance (FMA)
- Robustness tools (Noise factors to include in the FMEA)
- Interface analysis / Boundary Diagram
- Parameter Diagram
Methodology and hands on experience
- Path 1
- Item / Functions Requirements / Failure Modes / Effects of Failure / Severity
- Severity ranking guidelines review with best practices
- Actions for High Severity (9 / 10)
- Path 2
- Causes / Prevention Controls / Occurrence
- Quality-One ION Technique for Cause development
- Occurrence ranking Guidelines with Best Practices
- Actions to eliminate and/or reduce cause probability
- Special Characteristics definition (Key Dimensions / Features)
- Error Proofing and Mistake Proofing (Poka Yoke)
- Path 3
- Test and verification methods
- Detection ranking guidelines
- Actions to improve tests and verification techniques
- RPN reduction
DFMEA Closure
- Design Review integration (Design Review Based on Failure Modes (DRBFM) concepts)
- Test Plan development (Design Verification Plan and Report (DVP&R))
- Revisit RPN Rankings after action completion
Practical Application of PFMEA
Pre-work:
- Failure Mode Avoidance (FMA)
- Process Flow Chart
- Characteristic Matrix
- Lean Value Stream Map (optional)
Methodology and hands on experience
- Path 1
- Process Name / Functions Requirements / Failure Modes / Effects of Failure / Severity
- Severity ranking guidelines review with best practices
- Actions for High Severity (9 / 10)
- Path 2
- Causes / Prevention Controls / Occurrence
- Ishikawa (6M’s) and Use of Quality-One Matrix for Cause development
- Human Factors Engineering (Operator Error treatments)
- Occurrence ranking Guidelines with Best Practices
- Actions to eliminate and/or reduce cause probability
- Error Proofing for Human Error
- Path 3
- Test and verification methods for Causes and/or Failure Modes
- Detection ranking guidelines
- Actions to improve tests and verification techniques
Control Plan Relationships
- Pre-Launch Control Plan
- Production Control Plan
PFMEA Revisit FMEA RPN and Re-Rank
Managing FMEAs
- Family or Baseline FMEA / Legacy
- FMEA and 8D / Root Cause Analysis Relationship
Q&A and Closure
FMEA Training (Online)
– Technical Training Overview –
⇓ FMEA Training Course Details
⇓ FMEA Training Course Description
⇓ FMEA Training Course Objectives

FMEA Training Course Details (Online)
The Quality-One Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) Online Overview is completely interactive with audio, video, animation and downloadable reference materials. This option provides immediate access to FMEA content and is available 24 hours a day. The FMEA Online Overview is perfect for a basic introduction to FMEA or Subject Matter review.
FMEA Training Course Description (Online)
The FMEA Online Overview course is self-paced and interactive. The course explains the basic principles of FMEA, including structure and layout. The participant will be able to understand and manage risk, improve product and process quality, and improve customer satisfaction
The FMEA Online Overview follows a structured approach for identifying and prioritizing potential failure modes, taking action to prevent and detect failure modes and/or causes of failure. The course is interactive with video, audio, illustrations and downloadable templates and charts. The participant will have 30 days to complete the course and may access it as often as desired.
FMEA Training Course Objectives (Online)
After completing Quality-One’s onsite training courses, you should be able to:
- Explain Risk and its application in product development
- Describe the concepts required to conduct a FMEA
- Explain how FMEA teams are structured
- Tips and tricks for conducting an effective FMEA
- Identify FMEA inputs, functions, requirements and past failures
- Describe how failure modes, effects and causes are identified
- Explain how to assign rankings for Severity, Occurrence and Detection
- Identify mitigation actions for reducing Risks
- Explain how the Control Plan links to FMEA
FMEA Training Course Outline (Online)
Pre Test on FMEA knowledge
FMEA Process Overview
Introductions and course objectives
- The History and Purpose of FMEA
FMEA Methodology
- System / Subsystem / Component FMEA
- FMEA development methodology
- Quality-One FMEA Three Path Model
- Team structure and rules for efficiency
- Team membership for best results
FMEA Linkage and Collaboration
- The link between Design and Process FMEA
- Special Characteristics (critical and significant)
- Special Characteristics as inputs to PFMEA
- What is Risk?
- Criticality (Severity X Occurrence)
- Risk Priority Number (RPN) and its’ use
- When to take action and Developing Action Plans.
FMEA technique
Pre-work:
- Failure Mode Avoidance (FMA)
- Robustness tools (Noise factors to include in the FMEA)
- Interface analysis / Boundary Diagram
- Parameter Diagram
FMEA Methodology
- Path 1
- Item / Functions Requirements / Failure Modes / Effects of Failure / Severity
- Severity ranking guidelines review with best practices
- Actions for High Severity (9 / 10)
- Path 2
- Causes / Prevention Controls / Occurrence
- Occurrence ranking Guidelines with Best Practices
- Actions to eliminate and/or reduce cause probability
- Path 3
- Test and verification methods
- Detection ranking guidelines
- Actions to improve tests and verification techniques
- RPN Reduction
- Post Test
Learn More About FMEA Training
Quality-One offers Quality and Reliability Support for Product and Process Development through Consulting, Training and Project Support. Quality-One provides Knowledge, Guidance and Direction in Quality and Reliability activities, tailored to your unique wants, needs and desires. Let us help you Discover the Value of FMEA Consulting, FMEA Training or FMEA Project Support.
Additional resources: FMEA Training