Kaizen
– Continuous Improvement –

Introduction to Kaizen
Many companies are embracing Lean methodology. One of the main pillars of Lean methodology is Kaizen. Kaizen has been described in many ways, differing slightly in the definition for the word Kaizen, but keeping the overall idea of Kaizen the same. One definition states that it is actually two words: the first Kai, meaning change and the second Zen, meaning good. Another source stated that the definition of Kaizen is improving everybody, every day, everywhere. Yet another stated that Kaizen simply means to improve. Kaizen is improvement, improving processes, products, workplaces and people. We live in different world than our predecessors. Our world consists of technology that allows for instant communication around the globe. In this new and exciting time, we have opened up a truly global marketplace for goods and services. Competition for business is continually increasing. Today it is more important than ever to stand out from the crowd by offering the highest quality products at competitive prices. All businesses must continually seek out methods to increase quality and reduce waste.
What is Kaizen
Kaizen is more than just a methodology for continuous improvement. It is not a specific tool or set of tools to improve quality. Kaizen is a journey and not a destination. The objective of Kaizen is to improve productivity, reduce waste, eliminate unnecessary hard work and humanize the workplace. Kaizen is effective at identifying the three basic types of waste: Muda, Mura and Muri. Kaizen philosophy empowers everyone to assume responsibility for their processes and improve them. With Kaizen, workers at all levels of the organization are engaged in constantly watching for and identifying opportunities for change and improvement. Kaizen is not just a one-time event; more precisely, it is a process that occurs every day.
Kaizen has its roots in post war Japan. Following the Korean conflict, when Japan served as a major supply line for the US military, industry in Japan began to rebuild. The US aided in the revitalization of industry in Japan. In the early 1950s, W. Edwards Deming assisted Japanese business managers in developing quality systems utilizing statistical quality controls. At the heart of Kaizen is the Shewert Circle or Deming wheel that we now recognize as the PDCA cycle (Plan, Do, Check, Act). Kaizen began as part of the “Toyota Production System”, as a method to involve the entire workforce to improve product quality. Kaizen has since become one of the main factors for the country’s success. In Japanese companies, Kaizen is a way of life, involving everyone from the CEO all the way to the shop floor. In Japan, Kaizen is highly respected and considered instrumental in Japan becoming one of the strongest industrialized countries in the world.
Why Implement Kaizen
Throughout most companies today, there is a consistent drive to reduce waste and increase quality. The benefits of Kaizen methodology can reach far beyond reducing waste (muda) or increasing quality. Many different quality tools and disciplines can get you that far. Kaizen can take you farther. Properly implemented Kaizen methodology can achieve positive results in various ways at all levels of the organization. The advantages of implementing Kaizen include, but are not limited to:
- Utilization of Resources – Kaizen focuses on improving products through utilization of existing resources (your people) to achieve incremental and continuous improvement. Kaizen is centered around making small changes instead of relying on massive changes or expensive equipment investments to gain improvements.
- Increased Efficiency – Central to Kaizen methodology is the importance of providing a well-planned work area, eliminating unnecessary movement or operations and proper training for all employees.
- Employee Satisfaction – Kaizen is about creating an atmosphere of teamwork and change, where new ideas are encouraged. Team members are asked to really examine the processes and make suggestions for improvement.
- Safety Improvements – A safer work environment is another benefit of Kaizen. The safety improvements occur when new ideas to clean up and organize the work area are developed and implemented.
Kaizen involves everyone in the improvement effort. It does not rely on huge capital investments or attempt to make enormous strides at one time. The roots of Kaizen are in making small, immediate, incremental improvements in the processes and work standards. It is about looking for ways to improve every day. In due course, these small steps can result in giant leaps in quality, safety, efficiency, productivity and a positive impact on the bottom line.
How to Implement Kaizen
When most people think about how to implement Kaizen, the first thing they think is “Kaizen Event”. This is a short-term, focused activity targeting one particular process or department. This short event is also called a Kaizen Blitz (from the German word for lightning fast). While daily and event centered events are included, the core of Kaizen is not focused on one single event. Kaizen is a philosophy of good change that is incremental and continuously moving towards an ideal state. Kaizen is about looking for ways to improve every day by everyone.
Daily Kaizen vs. Kaizen Event
Daily Kaizen requires that the team meet on a regular basis, which could be daily or weekly. The team should discuss suggestions for improvement along with potential solutions for any issues encountered since the last meeting. Everyone on the team should participate and provide input to the meeting. You may choose to hold a special meeting or incorporate the discussion into a regularly occurring meeting. If possible, hold the meeting at the place where the process is occurring (Gemba Kaizen).
- While on a visit to a customer’s facility, one of our engineering teams observed an excellent example of the daily or weekly Kaizen. While touring the facility, the team noticed a large white board with several notes on it. When asked about these notes, the plant manager explained that the workers were encouraged to write suggestions on the board throughout the week. The team would gather weekly to discuss the ideas and determine which one to pursue. The selected idea would then be developed, applied and validated using the PDCA cycle. If the idea resulted in a measurable improvement, the worker who submitted the idea received a bonus. The plant manager enthusiastically went on to provide a few examples of improvements that were realized through this process. It became very apparent how much the entire organization had embraced gradual continuous improvement.
The Kaizen Event approach differs somewhat from the daily approach, although the goal is the same: improvement of the process. A Kaizen Event can generally be described as a few days or week long team-based rapid improvement activity. Thus, there is a definite start and stop to Kaizen Events. The event requires additional planning with a goal of implementing a more substantial change or improvement over the course of a few days or weeks.
Identifying Opportunities for Change
While the ultimate goal of Kaizen is gradual continuous improvement on a daily basis, you must start somewhere. When you first begin to implement Kaizen, you will likely need to perform process reviews to identify initial opportunities for improvement. The following are some basics for reviewing a process for possible improvement.
- Map the process – Obtain a process map / process flow chart and any work instructions, control plans or other process documentation that may exist. If you do not have a process map then build one. Gain a thorough understanding of the current state of the process. Find out what is really happening. If you do not understand your process, you cannot improve it. The Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (PFMEA) is a great place to find Kaizen opportunities. High Severity/Occurrence combinations and High RPN’s may be used for Kaizen activity.
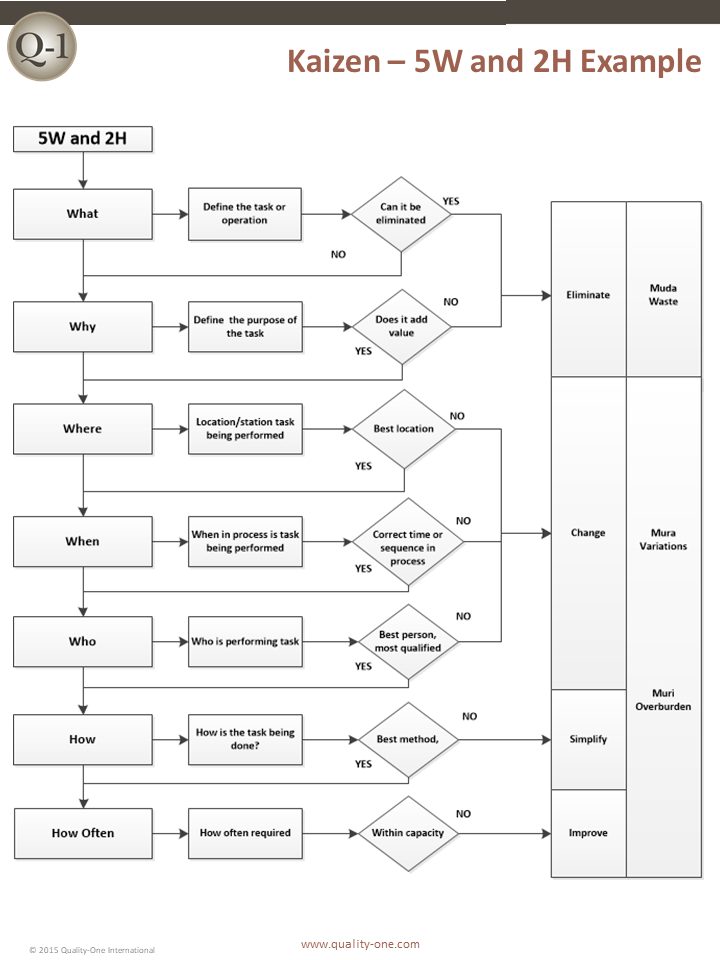
- Review the process – Review the process and evaluate each task or step. Using the 5 Why & 2 How model, ask the following questions:
- Why is the step being performed?
- What work is being performed / what value is being added?
- Where is the work currently being done / where should it be done?
- When is the process step being completed / when should it be completed?
- Who is performing the work / who should do the work?
- How is the work being done / how should it be done?
- How often is the process step performed / and how often does it need to be done?
Continue reviewing the process and each process step until you have covered each one. Learn to look past the current state and towards a future improved process. We must rid ourselves of the “we’ve always done it this way” mantra. Allowing this attitude will only prevent any change or improvement to your processes. By performing the process review and asking the right questions, you will be able to:
- Eliminate any unneeded steps or tasks from the process
- Combine process steps where possible; identify the process steps that must be performed discretely and those able to be completed in parallel
- Rearrange the sequence to reduce waste; in many cases, slight changes to the sequence or order of operations will enable us to eliminate wasted time and effort
- Simplify the process and utilize 5S where possible; often we can identify processes that could be completed in a simpler manner
- Validate the “good change”
Whichever Kaizen method you employ, be it daily or event based, the PDCA cycle should be followed for implementing continuous improvement:
- Plan: Identify an improvement opportunity and plan for the change
- Do: Carry out a small-scale process study to test the potential improvement and measure the results
- Check/Study: Review the results and measure the effectiveness of the change
- Act: Take action based on the results of the study
- If the change proves successful, implement it
- If the change did not work, repeat the cycle with a different solution
- Successful improvements should be reviewed for application that is more widespread – use the knowledge acquired to plan additional improvements and begin the cycle again
Mindset of Continuous Improvement
In summary, the goal of Kaizen is gradual continuous improvement. Implementing Kaizen and developing a mindset of continuous improvement within an organization is also gradual and should be continuous. The first step is to educate your workforce. Provide your teams with the proper Kaizen training, tools and system structure to allow them to succeed. Coach your employees and encourage them to become aware of problems and look for ways to improve every day. Through training and completion of the initial process reviews or Kaizen events, the team members likely will begin to take mental ownership of their individual processes. When this transfer of ownership takes place, the workers begin to think about possible improvements as their responsibility.
Learn More About Kaizen
Quality-One offers Quality and Reliability Support for Product and Process Development through Consulting, Training and Project Support. Quality-One provides Knowledge, Guidance and Direction in Quality and Reliability activities, tailored to your unique wants, needs and desires. Let us help you Discover the Value of Kaizen Consulting, Kaizen Training or Kaizen Project Support.